Coalition status
FSC Prohibited
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) is an international non-profit, mission –driven, multi-stakeholder organization founded in 1994 to promote…
Rainforest Risk MitigationSAN Risk MitigationThe SAN List of Pesticides for Use with Risk Mitigation is a product of U.S.A. public funding and the intellectual property of the analysis process…
UEBT Risk MitigationThe use of the Risk Mitigation Agrochemicals is discouraged as they are known to bear significant human health and environmental risks. Where these…
Details
Type: Pesticide
Use: Metabolite, Fungicide, Nematicide, Herbicide, Insecticide
Example applications: -
Example pests controlled: Nematodes;Various soil insects;Fungal pathogens;Weed seeds
Mode of action: Fumigant with contact action
Source: PPDB
Toxicty
Bird toxicity
Highly toxic to birds acute oral LD50 (LD50 < 200mg/bg bw)
Highly toxic to birds acute oral LD50 (LD50 < 200mg/bg bw)
Mammal toxicity
Acute oral LD50 for most sensitive mammal species (LD50 < 200mg/kg bw).
GHS safety labels
About Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)
From Wikipedia: The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and harmonized safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods with a host of information. The system acts as a complement to the UN Numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world.[1] This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.
- H301

Toxic if swallowed
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Oral - H314
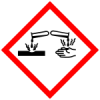
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
Class: Corrosion/irritation
Subclass: Skin - H317

May cause an allergic skin reaction
Class: Sensitization
Subclass: Skin - H331

Toxic if inhaled
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Inhalation - H400

Very toxic to aquatic life
Class: Aquatic
Subclass: Acute - H410

Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
Class: Aquatic
Subclass: Chronic
