Coalition status
FSC restricted HHPs
Chemical pesticide presenting one out of three of the following hazards: acute toxicity, chronic toxicity and environmental toxicity.
GCP-Phase-Out 2026Use of pesticides in the Phase-out List are reduced through use of Integrated Pest Management and phased out by 2030, if feasible. This includes…
Details
Type: Pesticide
Use: Herbicide
Example applications:
Example pests controlled:
Mode of action:
Source: PPDB
Toxicty
Mammal toxicity
Acute oral LD50 for most sensitive mammal species (LD50 < 200mg/kg bw).
GHS safety labels
About Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)
From Wikipedia: The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and harmonized safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods with a host of information. The system acts as a complement to the UN Numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world.[1] This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.
- H302

Harmful if swallowed
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Oral - H317

May cause an allergic skin reaction
Class: Sensitization
Subclass: Skin - H318
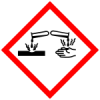
Causes serious eye damage
Class: (Corrosion)Damage/irritation
Subclass: Eye - H335

May cause respiratory irritation
Class: STOT-respiratory irritation
Subclass: Single exposure - H412
Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects
Class: Aquatic
Subclass: Chronic
