The Producer has a plan to phase out by 2024 pesticides listed in category 2 of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of…
Coalition status
Details
Toxicty
GHS safety labels
- H301

Toxic if swallowed
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Oral - H311

Toxic in contact with skin
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Dermal - H315

Causes skin irritation
Class: Corrosion/irritation
Subclass: Skin - H318
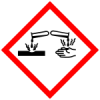
Causes serious eye damage
Class: (Corrosion)Damage/irritation
Subclass: Eye - H330

Fatal if inhaled
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Inhalation - H335

May cause respiratory irritation
Class: STOT-respiratory irritation
Subclass: Single exposure - H351

Suspected of causing cancer (state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard)
Class: Carcinogenicity - H361

Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child (state specific effect if known)(state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard)
Class: Toxic to Reproduction - H372

Causes damage to organs (state all organs affected, if known) through prolonged or repeated exposure (state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard)
Class: STOT
Subclass: Repeated exposure - H400

Very toxic to aquatic life
Class: Aquatic
Subclass: Acute - H410

Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
Class: Aquatic
Subclass: Chronic
