The Producer has a plan to phase out Pesticides defined as…
Coalition status
BCI have plan to phase out
Fairtrade Red
This list contains 207 pesticides. The list is valid as of January 2018.
Prohibited pesticides that must not be used on Fairtrade products under any…
FSC restricted HHPsChemical pesticide presenting one out of three of the following hazards: acute toxicity, chronic toxicity and environmental toxicity.
GCP ProhibitedPesticides in the Prohibited List are not used.
This includes pesticides that are:
Listed under the Stockholm Convention, Rotterdam Convention or…
Rainforest prohibited PesticidesSAN HHP: phase-outThe SAN List of Highly Hazardous Pesticides consists of 230 pesticides:
SAN HHP Pesticides are classified as Highly Hazardous Pesticides according to…
UEBT ProhibitedThe use of Prohibited Agrochemicals is prohibited for certified, prioritised and verified ingredients, because they are considered Highly Hazardous…
UTZ ProhibitedA pesticide all uses of which have been prohibited by final regulatory action, in order to protect human health or the environment.
Details
Type:
Use: Other substance
Example applications:
Example pests controlled:
Mode of action: Unclear but thought to damage genetic material
Source: PPDB
Toxicty
EPA: Probable Human Carcinogen
Agents with sufficient evidence (i.e., indicative of a causal relationship) from animal bioassay data, but either limited human evidence (i.e.,…
GHS carcinogen
Category 1A: the assessment is based primarily on human evidence
IARC Group 2A
This designation is applied when there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans as well as sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in…
GHS safety labels
About Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS)
From Wikipedia: The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and harmonized safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods with a host of information. The system acts as a complement to the UN Numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world.[1] This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.
- H226

Flammable liquid and vapour
Class: Flammable
Subclass: Liquids - H301

Toxic if swallowed
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Oral - H311

Toxic in contact with skin
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Dermal - H314
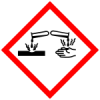
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
Class: Corrosion/irritation
Subclass: Skin - H317

May cause an allergic skin reaction
Class: Sensitization
Subclass: Skin - H331

Toxic if inhaled
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Inhalation - H350

May cause cancer (state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard)
Class: Carcinogenicity
