The Producer has a plan to phase out Pesticides defined as…
Coalition status
Details
Toxicty
GHS safety labels
- H301

Toxic if swallowed
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Oral - H311

Toxic in contact with skin
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Dermal - H314
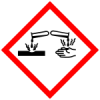
Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
Class: Corrosion/irritation
Subclass: Skin - H317

May cause an allergic skin reaction
Class: Sensitization
Subclass: Skin - H331

Toxic if inhaled
Class: Acute Toxicity
Subclass: Inhalation - H341

Suspected of causing genetic defects (state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard)
Class: Germ Cell Mutagenicity - H350

May cause cancer (state route of exposure if it is conclusively proven that no other routes of exposure cause the hazard)
Class: Carcinogenicity
